Exercícios
Limites no infinito e Assíntotas horizontais
Selecione os exercícios por
Dificuldade
Categoria
Outros
Os botões acima permitem selecionar que tipos de exercício você deseja ver na lista.
Para retirar alguma categoria da lista, clique sobre o botão para toná-lo inativo. Para adicioná-la, clique novamente no botão.
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }3^{x}$.
$\infty$.
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\log _{3}x$.
$\infty$.
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{5x^{3}-6x-3}{6x^{2}+28x+2}$.
$\infty$
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 0,27\right) ^{x}$.
$0$.
Encontre os seguintes limites em termos do número $\alpha = \displaystyle \lim_{n \to 0} \dfrac{\sin x}{x}$.
$\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty} \dfrac{\sin x}{x}$.
$\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty} x \sin \left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)$.
Defina ``$\displaystyle \lim_{x \to -\infty} f(x) = l$''.
Ache $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to -\infty} \dfrac{a_n x^n + \ldots + a_0}{b_m x^m + \ldots + b_0}$.
Mostre que $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to \infty} f(x) = \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -\infty} -f(x)$.
Mostre que $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0^-} \dfrac{1}{f(x)} = \displaystyle \lim_{x \to -\infty} f(x)$.
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\ln \dfrac{x}{x+1}$.
$0$
Classifique as afirmações a seguir como verdadeiras ou falsas:
Se $ \lim\limits_{x\to \infty} f(x) = 5$, então estamos implicitamente afirmando que o limite em questão existe.
$\infty/0$ não é uma forma indeterminada.
Verdadeira
Verdadeira
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty }\dfrac{5-x}{2x+3}$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{x+3}$
- $-1/2$
- $0$
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 2^{x}-3^{x}\right) $.
$-\infty$.
Calcule os seguintes limites. Pode ser útil usar a relação de inversão que há em relação às funções logarítmicas e exponenciais (isto é, $\ln(x)=y \Leftrightarrow e^y=x$) e/ou gráficos.
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow\infty}\log_3 x$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 0^+}\ln x$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty}e^x$
Um tanque contém 5000 litros de água pura. Água salgada contendo $30$g de sal por litro de água é bombeada para dentro do tanque a uma taxa de $25$ L$/$min. Considerando o tempo $t$ em minutos, mostre que a concentração de sal $C$ em função de $t$ (em gramas por litro) é dada por:$$C(t) = \dfrac{30 t}{200+t}.$$
O que acontece com a concentração para um tempo muito grande, isto é, para $t \to \infty$?
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{1-2^{x}}{1-3^{x}}$.
$0$.
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty }\left( 2^{x}+2^{-x}\right) $.
$-\infty$.
Calcule o limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{2}+4x}\right)$.
$-\infty$.
Considere a função $f(x) = 2^x+10$. Calcule os seguintes limites e, depois, discuta se a função $f(x)$ tem assíntotas horizontais.
$\lim\limits_{x\to -\infty} f(x)$.
$\lim\limits_{x\to \infty} f(x)$.
1. $10$.
2. $\infty$
Possui assíntota horizontal de equação $y=10$,
Avalie os seguintes limites de acordo com o gráfico da função:
$f(x) = \frac{1}{e^x+1}$
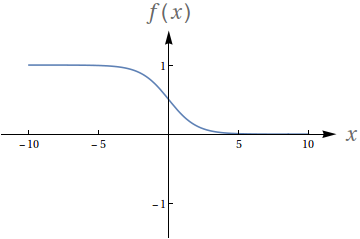
$\lim\limits_{x\to -\infty} f(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to \infty} f(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to 0^-} f(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to 0^+} f(x)$
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{3x^{3}+2x-1}}{\sqrt{x^{2}+x+4}}$.
$\sqrt[3]{3}$
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{x}\right) ^{x+2}$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 1+\dfrac{1}{2x}\right) ^{x} $
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( \dfrac{x+2}{x+1}\right) ^{x}$
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 5+\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{4}{x^{2}}\right)$.
$5$
O gráfico a seguir representa o número de indivíduos de uma população ao longo do tempo.
Pode-se dizer que há uma assíntota horizontal para essa população? Justifique.
O que essa assíntota representa em termos biológicos? (Isto é, qual a interpretação da assíntota em função da população?)
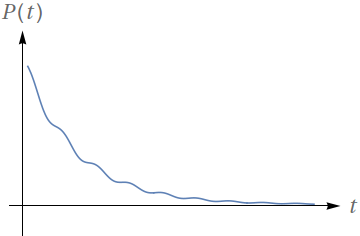
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\to e} \ln x$, em que $e$ é o número de Euler.
$1$.
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{2}+3}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{2}+3}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty } \left( \sqrt{x+1}-\sqrt{x+3}\right)$
- $0$
- $-\infty$
- $0$
Construa os gráficos das funções indicadas e calcule os limites:
$ f(x)=x^2$ quando $x\rightarrow\infty$
$ h(x)=3x^5$ quando $x\rightarrow -\infty$
$g(y)=\tan^{-1}(y)$ quando $y\rightarrow\infty$
$f(x)=\frac{1}{x}$ quando $x\rightarrow -\infty$
$f(x)=\frac{1}{x^7}$ quando $x\rightarrow \infty$
$f(x)=\frac{1}{x^{-2}}$ quando $x\rightarrow \infty$
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\log _{3}x$.
$\infty$.
O gráfico da função $f(x)=\frac{x^3+2x^2+1}{5-x^2}$ possui alguma assíntota horizontal?
Não possui.
Avalie os seguintes limites de acordo com o gráfico da função:
$f(x) = \cos (x)$
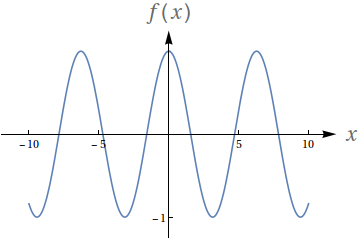
$\lim\limits_{x\to -\infty} f(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to \infty} f(x)$
Determine todas as assíntotas horizontais da função $f(x) = \frac{x^2-1}{-x^2-1}$.
$y=-1$.
A função $f(x) = \left\{ \begin{array}{ccc} x^2-1 & & x < 3 \\x+5 & & x\geq 3 \end{array}\right.$ é contínua em todo o seu domínio? Justifique.
Sim, é. O único ponto em que não poderia (inicialmente) ser contínua é em $x=3$. Todavia, temos $\lim\limits_{x\to 3^-} f(x)=\lim\limits_{x\to 3^+} f(x)=f(3)=8$.
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{5x^{4}-2x+1}{4x^{4}+2x+3}$.
$5/4$
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 5-3x+4x^{2}-x^{3}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{5x^{3}-6x-3}{6x^{3}+2}$
- $-\infty$
- $5/6$
Calcule os limites indicados dividindo o numerador e o denominador por uma potência conveniente de $x$. Como esses limites se relacionam com as mais altas potências do numerador e do denominador?
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow\infty}\frac{x^4-2}{3x^4-x^3+1}$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow\infty}\frac{\sqrt{2x^6-2x+1}}{x^3-x^2+2}$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty}\frac{\sqrt{x^2-3}}{x+1}$
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }3^{x}$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 2^{x}-3^{x}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( 0,27\right) ^{x}$
1. $\infty$.
2. $-1$.
3. $0$.
Calcule o limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow +\infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{2}+4x}\right)$.
$-2$.
Seja $N$ um número positivo tal que, para cada $x$ no intervalo $(N,+\infty)$, os valores da função $f(x)=1/x^2$ estejam no máximo a $0,1$ unidade de $L=0$. Encontre $N$.
Seja $N$ um número positivo tal que, para cada $x$ no intervalo $(N,+\infty)$, os valores da função $f(x)=x/(x+1)$ estejam no máximo a $0,01$ unidade de $L=0$. Encontre $N$.
Seja $N$ um número positivo tal que, para cada $x$ no intervalo $(-\infty,N)$, os valores da função $f(x)=1/x^3$ estejam no máximo a $0,001$ unidade de $L=0$. Encontre $N$.
Seja $N$ um número positivo tal que, para cada $x$ no intervalo $(-\infty,N)$, os valores da função $f(x)=x/(x+1)$ estejam no máximo a $0,001$ unidade de $L=0$. Encontre $N$.
Calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{3}+2}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x^{2}+2}\right)$
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\left( x-\sqrt{x+2}\right)$
- $-\infty$
- $0$
- $\infty$
Verifique se os seguintes limites existem. Explique.
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow\infty}2^{1/x}$.
$\lim\limits_{t\rightarrow\infty}\sin x$.
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow 2^-}\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{1}{2x-4}\right)$.
Avalie os seguintes limites de acordo com o gráfico da função:
$f(x) = x^2\sin (\pi x)$
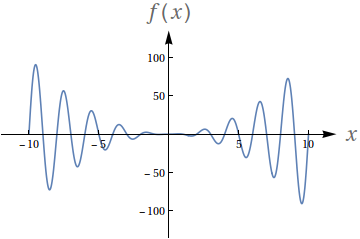
$\lim\limits_{x\to -\infty} f(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to \infty} f(x)$
É possível mostrar que, sob certas condições, a velocidade $v(t)$ de uma gota de chuva caindo no instante $t$ é:
$$v(t) = v^\star \left(1-\exp\left(-\dfrac{gt}{v} \right)\right),$$
onde $g$ é a aceleração da gravidade e $v^\star$ é a velocidade final da gota.
Calcule a velocidade para um tempo muito grande, isto é, calcule $\displaystyle \lim_{t \to \infty} v(t)$.
Considerando $v^\star = 1$m$/$s e $g=9,8$m$/$s$^2$, faça o gráfico de $v(t)$. Quanto tempo levará para a velocidade da gota atingir $99\%$ de sua velocidade final?
Calcule o seguinte limite:
$\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow \infty }\dfrac{1-2^{x}}{1-3^{x}}$.
$0$.
Sabemos que limites que tomam a forma indeterminada ``$\infty-\infty$" exigem um pouco mais de trabalho para serem calculados. Calcule, de forma adequada, o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow\infty}\left(\sqrt{2x^2-7}-x\right)$.
Sabendo que $\lim\limits_{x\to2} f(x) = 3$ e $\lim\limits_{x\to2} g(x) = -1$, calcule os seguintes limites:
$\lim\limits_{x\to2}(f+g)(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to2}(fg)(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to2}(f/g)(x)$
$\lim\limits_{x\to2}f(x)^{g(x)}$
Calcule o limite $\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow -\infty }\left( 2^{x}+2^{-x}\right)$.
$\infty$.

